-
 What are Lipids - Body Fat ??
What are Lipids - Body Fat ??
What are Lipids?

Lipids are a fat like substance found in the blood stream or stored in the body. Lipids are derived from two main sources, exogenously from food and endogenously made in the liver. Lipids are essential for many body functions such as building cell membranes, brain functioning and to synthesize hormones.
If the lipids are excessive these can stick to the blood vessel walls and form a buildup called plaque, which can block the blood flow to the heart or brain and cause heart attack or stroke.
Lipids are molecules that contain hydrocarbons and make up the building blocks of the structure and function of living cells. Examples of lipids include fats, oils, waxes, certain vitamins, hormones and most of the non-protein membrane of cells.
The two types of lipids are:
- LDL or the bad cholesterol transports cholesterol to tissues and arteries where the cholesterol can create blockages and hence is bad. In other words Low Density Lipoprotien is Bad Cholesterol.
- HDL or the good cholesterol. This prevents the build up of cholesterol in the blood vessels; higher the HDL the better it is.
Triglycerides: When high these can be associated with a higher risk of heart disease.
Natural supplements to help control lipids:
Some of the dietary changes shown to have a beneficial effect are:
- Eating fatty fish or taking Omega 3 fatty acid supplements can lower triglcyerides
- Increasing the daily fiber intake and intake of oatmeal can lower LDL cholesterol
- Intake of walnuts in moderation helps to lower the LDL cholesterol.
- Oils which are healthy to eat are olive oil, rice bran oil and cannola oils which have a high content of monounsaturated fats.
Though these are natural supplements, these should be taken with the advice of a doctor or nutritionist familiar with your lipid levels.
What are lipids soluble in?
Lipids are not soluble in water. They are non-polar and are thus soluble in nonpolar environments like in choloroform but not soluble in polar environments like water.
What do lipids consist of?
Lipids have mainly hydrocarbons in their composition and are highly reduced forms of carbon. When metabolized, lipids are oxidized to release large amounts of energy and thus are useful to living organisms.
Where do lipids come from?
Lipids are molecules that can be extracted from plants and animals using nonpolar solvents such as ether, chloroform and acetone. Fats (and the fatty acids from which they are made) belong to this group as do other steroids, phospholipids forming cell membrane components etc.
Hydrolyzable/Non-hydrolyzable lipids
Lipids that contain a functional group ester are hydrolysable in water. These include neutral fats, waxes, phospholipids, and glycolipids. Nonhydrolyzable lipids lack such functional groups and include steroids and fat-soluble vitamins (e.g. A, D, E, and K). Fats and oils are composed of triacylglycerols or triglycerides. These are composed of glycerol (1,2,3-trihydroxypropane) and 3 fatty acids to form a triester. Triglycerides are found in blood tests. Complete hydrolysis of triacylglycerols yields three fatty acids and a glycerol molecule.
Fatty acids
Fatty acids are long chain carboxylic acids (typically 16 or more carbon atoms) which may or may not contain carbon-carbon double bonds. The number of carbon atoms are almost always an even number and are usually unbranched. Oleic acid is the most abundant fatty acid in nature.

The membrane that surrounds a cell is made up of proteins and lipids. Depending on the membrane’s location and role in the body, lipids can make up anywhere from 20 to 80 percent of the membrane, with the remainder being proteins. Cholesterol, which is not found in plant cells, is a type of lipid that helps stiffen the membrane. Image Credit: National Institute of General Medical Sciences
Waxes/fats and oils
These are esters with long-chain carboxylic acids and long-alcohols. Fat is the name given to a class of triglycerides that appear as solid or semisolid at room temperature, fats are mainly present in animals. Oils are triglycerides that appear as a liquid at room temperature, oils are mainly present in plants and sometimes in fish.
Mono/poly unsaturated and saturated
Those fatty acids with no carbon-carbon double bonds are called saturated. Those that have two or more double bonds are called polyunsaturated. Oleic acid is monounsaturated.
Saturated fats are typically solids and are derived from animals, while unsaturated fats are liquids and usually extracted from plants.
Unsaturated fats assume a particular geometry that prevents the molecules from packing as efficiently as they do in saturated molecules. Thus the boiling points of unsaturated fats is lower.
Synthesis and function of lipids in the body
Lipids are utilized or synthesized from the dietary fats. There are in addition numerous biosynthetic pathways to both break down and synthesize lipids in the body.
There are, however, some essential lipids that need to be obtained from the diet. The main biological functions of lipids include storing energy as lipids may be broken down to yield large amounts of energy. Lipids also form the structural components of cell membranes and form various messengers and signalling molecules within the body.
-

Thanks for sharing information about Lipid or Body Fats. Actually, each of us should be knowledgeable on this matter because this kind of information is so important to understand the caused and effect if we happen to restore of this body fats. Some are good while many are not good in the long run as they can give us some conditions that are not so good for our body.
-

thats a wonderful information being shared here as it has accelerated my knowledge related to fat and cholestrol of the body
 Posting Permissions
Posting Permissions
- You may not post new threads
- You may not post replies
- You may not post attachments
- You may not edit your posts
-
Forum Rules






 Reply With Quote
Reply With Quote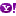

Bookmarks